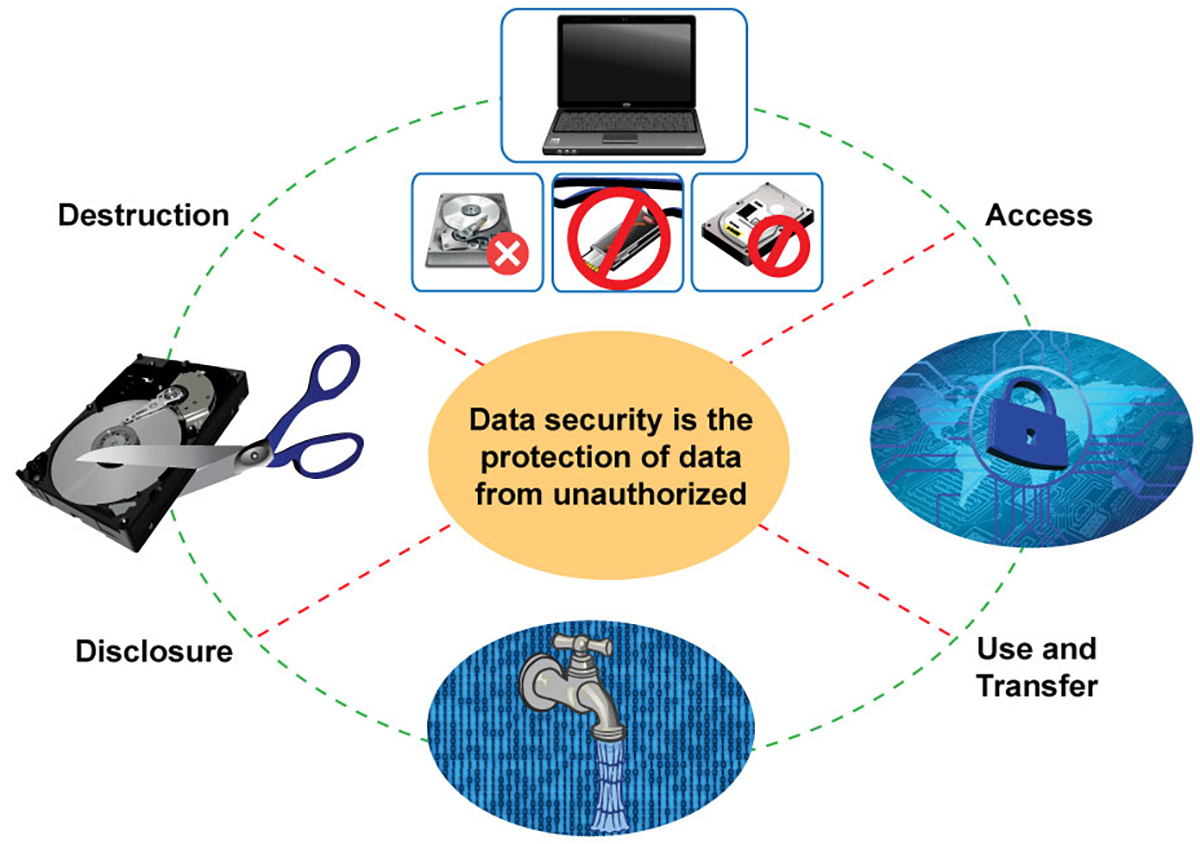
Data Security, Storage, Access, Transfer and Destruction
- Network security: Keeping confidential data off the Internet and in extreme cases, store sensitive materials on computers not connected to the internet.
- Physical security: Restricting access to buildings and rooms where computers or media are kept. Only let trusted individuals troubleshoot computer problems.
- Computer systems and files: Maintaining virus protection software up-to-date, don't send confidential data via email (or, if you must, use encryption), set passwords on files and computers, react with skepticism to phone calls and emails that claim to be from your institution's IT department.
IT College Representatives
Database Storage and Disposal Recommendations
Florida Atlantic Supportive Storage Options
- BHRIC - Biomedical Health Research Informatics Core
- HPC - High Performance Computing
-
KOKO Software Modules - KoKoSec
To gain access to Koko, click here.
Data Access
The research plan should determine which personnel will have access to the data.
Principal investigators should have clearly established who controls the data (e.g., the PI, a student, lab personnel, university, or sponsor).
The IRB protocol should specify whether any outside parties will have access to study data and the process for storing and/or transferring that data.
Data Sharing and Transfer
- Required by publishers (e.g., Cell, Nature, Science).
- Required by government funding agencies (e.g., NIH, NSF).
- Allows data to be used to answer new questions.
- Makes research more open.
- Makes your papers more useful and citable by other researchers.
Data transmission needs a plan to protect the confidentiality of the data.
Research teams are advised to develop standard operating procedures regarding a secure transmission process regardless of the data being anonymous, coded or non-sensitive.
Secure data transmission processes are a best practice and mitigate the potential of data breaches.
Florida Atlantic provides extensive guidance, software and resources to assist researchers to encrypt and transfer data.
How to Share Data?
Transfer of De-Identified Data
Responsibilities Beyond Research Team
Prior to data access, students and external investigators not explicitly listed in the IRB data access listing should:
Note: This must all be documented electronically or on paper, approved by the PI and the data manager should be informed.
Note: The data manager will create an individual folder on the secure server or cloud server for each separate study project.
Responsibilities of the Principal Investigator
- Verify documents listed above are complete.
- Make sure DUA is in place.
- Create an individual folder on the secure server or cloud server for each separate study project.
- Create the data set with a mapped set of Identification numbers (NEWID) without personal identifiers.
- Safeguard the Identification key. It will not be on a personal computer.
- According to the data use timeline or DUA or the research plan, send an email to the student or scientist and ask them to delete the data set. This email will be kept on file for the record.
Data Retention and Destruction
 OHRP: 45 CFR 46 requires research records to be retained for at least 3 years after the completion of the research.
OHRP: 45 CFR 46 requires research records to be retained for at least 3 years after the completion of the research.
 HIPAA: Records must be retained for a minimum of 6 years after each subject signed an authorization.
HIPAA: Records must be retained for a minimum of 6 years after each subject signed an authorization.
 FDA: Records must be retained for a period of 2 years following the date a marketing application is approved for the drug for the indication.
FDA: Records must be retained for a period of 2 years following the date a marketing application is approved for the drug for the indication.
 VA: Records must be retained indefinitely per VA federal regulatory requirements.
VA: Records must be retained indefinitely per VA federal regulatory requirements.
 Sponsor Requirements – contract: PI must insure that he/she complies with any terms for record retention detailed in the contract.
Sponsor Requirements – contract: PI must insure that he/she complies with any terms for record retention detailed in the contract.
Competent data destruction services should be used to ensure that no data could be recovered from old electronic media. The U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) 5220.22-M standard for permanently removing data from disks is considered the most rigorous standard. DoD-compliant disk sanitization software may be used to overwrite or wipe data content from electronic media. Note: free versions of this kind of software may not be DoD-compliant.